 |
|
|
| Basic Robotics |
| Robotics encompasses many technical disciplines. Including
electrical hardware, software, mechanical hardware
including human factor issues, various forms of sensors (position
, velocity, force, displacement ….)
Various Robot types
- Industrial
- Autonomous
- Mobile
- Surgical
- Tele-robot
Industrial
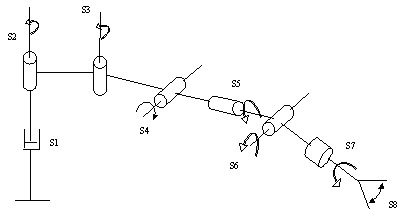
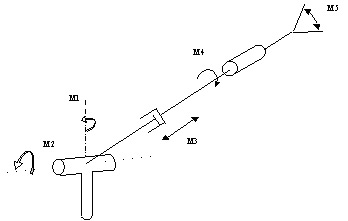
There are primarily two types of industrial robots: 1- The ones used in automotive industry for painting, welding, and other manufacturing tasks, and 2- The ones used in microelectronics industry used primarily for preceision and speedy assemblies. The diagrams below show an example of a robotic arm having eight joints. Each joint in this case has one degree of freedom. Of course there joints with two degrees of freedom (e.g. a U-joints) and joints with three degrees of freedom (e.g. spherical joints). |
|
|
 |
| Resources |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z = 4 . sin(a) . sin(q2)
. tan2(j) + 3 . sin(a) . cos(q2) . tan2(j)
|
|

